To track hurricanes, use reliable resources such as the National Hurricane Center (NHC) or Weather.com. These sites provide up-to-date information on hurricane tracking, including storm location, intensity, and forecasted path.
Additionally, you can use mobile apps like Hurricane Tracker or Storm Radar for real-time updates on hurricanes and their trajectories. Tracking hurricanes is crucial for individuals, emergency responders, and communities in hurricane-prone areas. By monitoring the movements and intensity of these powerful storms, people can make informed decisions to protect themselves and mitigate any potential damage.
But how exactly can you track hurricanes? We will explore various methods to track hurricanes accurately and efficiently. By utilizing reliable resources and technology, you can stay informed about the latest developments and prepare yourself for the impact of these natural disasters. Whether you’re a weather enthusiast, a concerned citizen, or a government agency, tracking hurricanes is essential for ensuring safety and minimizing the destruction caused by these ferocious storms. So, let’s dive into the different ways you can track hurricanes and stay ahead of the storm.
Understanding Hurricanes
Understanding hurricanes and how to track them is crucial for preparedness and safety. Stay informed and utilize reliable resources to monitor their path and intensity, ensuring you are ready to take necessary precautions when a hurricane is approaching.
Differentiating Hurricanes From Other Tropical Storms
- Hurricanes are powerful tropical cyclones that form in the ocean and are characterized by sustained winds exceeding 74 miles per hour (119 km/h).
- Unlike other tropical storms, hurricanes have a distinct eye at the center, which is a relatively calm area surrounded by a wall of clouds.
- They are larger in size compared to other tropical storms and can span hundreds of miles in diameter.
- Hurricanes are classified into different categories based on their wind speed and potential for damage, with Category 5 being the most intense.
The Anatomy Of A Hurricane
- The eye of a hurricane is a circular area of calm weather and clear skies in the center of the storm. It can range in diameter from a few miles to more than 60 miles (100 km).
- The eyewall surrounds the eye and is the most dangerous part of the hurricane. It contains the strongest winds, heaviest rainfall, and the greatest potential for tornadoes.
- Bands of clouds, known as rainbands, spiral outward from the eyewall, bringing intense rainfall and gusty winds. These rainbands can extend for hundreds of miles from the center of the storm.
The Science Behind Hurricane Formation
- Hurricanes form over warm ocean waters as low-pressure systems with rotating winds. The warm water provides the necessary energy for the storm to develop and strengthen.
- As moist air rises from the ocean’s surface, it cools and condenses, forming clouds and releasing heat energy. This heat energy fuels the storm, causing it to intensify.
- The rotation of the Earth, known as the Coriolis effect, plays a crucial role in shaping the structure of a hurricane. It causes the storm to spin counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
Factors Influencing Hurricane Development
- Warm ocean waters are essential for hurricane formation and growth. The temperature of the water needs to be at least 80 degrees Fahrenheit (27 degrees Celsius) to provide the necessary heat energy.
- Favorable atmospheric conditions, such as low wind shear (the change in wind speed and direction with altitude), help maintain the structure and strength of the storm.
- Moisture in the atmosphere is required for the formation of clouds and precipitation within the hurricane. Dry air can weaken or even dissipate a storm.
- The absence of strong upper-level winds can allow a hurricane to intensify by allowing the warm air to rise freely and create a stable structure.
Understanding hurricanes is crucial for tracking and predicting their behavior. By differentiating hurricanes from other tropical storms, understanding their anatomy, and exploring the science behind their formation, we gain valuable insights into these powerful natural phenomena. Factors such as warm ocean waters, atmospheric conditions, and moisture all contribute to the development and strength of hurricanes.
Armed with this knowledge, we can better prepare for the potential impacts of these formidable storms.
Tracking Hurricane Formation
Hurricane formation can be tracked through satellite imagery, weather models, and data from buoys and aircraft, providing valuable information for forecasting and preparedness.
Tracking hurricane formation is crucial for understanding and predicting the intensity and impact of these powerful storms. By monitoring atmospheric conditions, recognizing tropical disturbances and depressions, and identifying tropical storms and hurricanes, scientists and meteorologists can utilize satellite imagery and weather data to track and analyze their development.
In this section, we will explore these key components of tracking hurricane formation.
Monitoring Atmospheric Conditions
Tracking hurricanes begins with monitoring the atmospheric conditions that facilitate their formation. Here are the key factors to consider:
- Warm ocean waters: Hurricanes thrive on warm water temperatures of at least 80°F (27°C), providing the necessary energy for their formation and intensification.
- Low wind shear: Limited wind shear, which refers to the difference in wind speed and direction at different altitudes, allows hurricanes to maintain their structure and continue developing.
- Moisture and humidity: High levels of moisture in the atmosphere contribute to the formation and sustenance of hurricanes by supplying the necessary fuel for their growth.
Recognizing Tropical Disturbances And Depressions
Tropical disturbances are the preliminary stage of hurricane formation. These broad areas of low pressure in the atmosphere can develop into more organized systems. Here’s what to look for:
- Clusters of thunderstorms: Groups of thunderstorms often represent the initial signs of a tropical disturbance. These storms release heat and energy, which contributes to the formation of low-pressure systems.
- Disorganized cloud formations: At this stage, cloud formations are typically unorganized and lack a defined rotation. However, they still possess the potential for further development into tropical depressions and storms.
Identifying Tropical Storms And Hurricanes
As tropical disturbances become more organized, they progress into tropical depressions and eventually tropical storms or hurricanes. Here’s how to distinguish between these stages:
- Tropical depressions: When a tropical disturbance becomes more organized and exhibits a noticeable cyclonic circulation, it is classified as a tropical depression. Winds in a depression range between 23 and 39 mph (37-63 km/h).
- Tropical storms: If a depression’s winds exceed 39 mph (63 km/h), it is upgraded to a tropical storm. At this stage, the storm develops a more recognizable structure, with a clear center of circulation and increased rainfall.
- Hurricanes: When sustained winds in a tropical storm reach or exceed 74 mph (119 km/h), it is designated as a hurricane. Hurricanes are further classified on the Saffir-Simpson scale based on their intensity, ranging from Category 1 (weakest) to Category 5 (strongest).
Utilizing Satellite Imagery And Weather Data
To track the formation, movement, and intensity of hurricanes, meteorologists rely on satellite imagery and weather data. Here’s how these tools contribute to the tracking process:
- Satellites: Advanced weather satellites provide valuable visual data on cloud formation, temperature distribution, and atmospheric conditions, allowing scientists to monitor the development and movement of hurricanes in real-time.
- Weather stations and buoys: Ground-based weather stations and ocean buoys collect vital data on wind speed, air pressure, humidity, and temperature, providing valuable insights into the dynamics of a developing or existing hurricane.
- Models and forecasting: Meteorologists utilize complex computer models, incorporating data from satellites and weather stations, to simulate and predict the path, intensity, and potential impact of hurricanes. These forecasts aid in decision-making and alerting communities in potential danger zones.
Tracking hurricane formation involves meticulous observation, analysis, and interpretation of various atmospheric indicators and data sources. Through continuous monitoring and the application of sophisticated tools, scientists strive to enhance our understanding of hurricanes and improve our ability to predict their behavior.
Predicting Hurricane Paths
Hurricane paths can be tracked through advanced forecasting techniques and satellite imagery, enabling accurate predictions. Tracking hurricanes assists in issuing timely warnings and ensuring preparedness for potential impact.
Understanding The Cone Of Uncertainty:
The cone of uncertainty is a visualization tool used by meteorologists to depict the potential path of a hurricane. It represents the area where the center of the storm could be located. Here are some key points to help you understand the cone of uncertainty:
- A hurricane’s path is uncertain, especially several days in advance. The cone of uncertainty shows the range of possible tracks, accounting for forecasting errors.
- The cone is constructed based on historical data and various computer models that take into account atmospheric conditions, land masses, and other factors.
- The cone widens as the forecast extends further into the future since there is more uncertainty over time.
- It’s important to note that the cone is not indicative of the size or impacts of the storm; rather, it focuses on the potential path the hurricane may take.
Analyzing Hurricane Models And Forecasts:
Meteorologists use a combination of models and forecasts to predict the path of a hurricane. Here are the key aspects involved in analyzing these models and forecasts:
- Numerical models: Meteorologists rely on sophisticated computer models that simulate the behavior of the atmosphere. These models take into account a multitude of variables to predict the path, intensity, and timing of a hurricane.
- Ensemble models: Ensemble models generate multiple simulations with slight variations in initial conditions. This allows forecasters to assess the range of possibilities and evaluate the uncertainty in the predictions.
- Satellite data: Satellite imagery provides crucial information about a hurricane’s structure, cloud patterns, and developing eye, helping forecasters track its movement more accurately.
- Historical analysis: Forecasters analyze past hurricane tracks and characteristics to discern patterns and improve their understanding of how storms behave.
Interpreting National Hurricane Center Advisories:
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the primary authority responsible for issuing advisories and warnings related to hurricanes. Here’s what you need to know about interpreting NHC advisories:
- Track forecast: NHC advisories include the forecasted track of the hurricane, presented as a line or a series of dots. This track represents the most likely path, taking into account meteorological data and models.
- Forecast uncertainty: NHC advisories also incorporate the cone of uncertainty, indicating the range within which the center of the storm is likely to stay. The size of the cone depends on the forecast time frame and the level of forecast confidence.
- Intensity forecast: NHC advisories provide information about the predicted intensity of the hurricane, including maximum sustained winds, storm surge potential, and rainfall amounts.
- Watches and warnings: NHC advisories issue watches and warnings to inform the public of potentially dangerous conditions. A hurricane watch means that hurricane conditions are possible in the specified area, while a warning indicates that hurricane conditions are expected within the next 36 hours.
Tracking changes in storm intensity:
In addition to predicting the path of a hurricane, it’s crucial to track changes in its intensity. Here’s why keeping an eye on storm intensity is important:
- Evolving threat: Monitoring changes in storm intensity allows forecasters to assess the potential impact on coastal regions, plan evacuation strategies, and issue appropriate warnings.
- Rapid intensification: Hurricanes can undergo rapid intensification, transforming from a weaker system into a major hurricane within a short period. Tracking these changes helps provide timely and accurate information to the public.
- Forecast adjustments: Changes in storm intensity may require adjustments to evacuation plans, emergency resource allocation, and public advisories. Being aware of these changes helps ensure the safety of those in the storm’s path.
- Potential risks: Storm surges, heavy rainfall, and high winds are all factors that can lead to life-threatening situations. Monitoring storm intensity helps to predict and prepare for these risks.
Remember, understanding the cone of uncertainty, analyzing hurricane models and forecasts, interpreting NHC advisories, and tracking changes in storm intensity are all essential components in predicting and tracking hurricanes. By following these steps, meteorologists can provide timely and accurate information to help communities prepare and mitigate the impact of these powerful storms.
Essential Tools For Tracking Hurricanes
Successfully track hurricanes with these essential tools. Stay informed and prepared with reliable hurricane tracking technology.
Tracking hurricanes is crucial for both emergency management officials and individuals living in hurricane-prone areas. To accurately monitor these powerful storms, it is essential to utilize a range of tools and resources. Here are some of the key tools and technologies that can assist in tracking hurricanes:
Weather Tracking Websites And Apps:
- National Hurricane Center (NHC) website: Established by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), this site provides comprehensive information on current and forecasted hurricane activity. It offers real-time storm updates, satellite imagery, and storm track models.
- The Weather Channel: As a popular weather website and app, The Weather Channel offers interactive maps, storm forecasts, and hurricane alerts. It also provides educational content and safety tips for hurricane preparedness.
- Windy.com: This website provides detailed and visually appealing hurricane tracking maps. Users can easily access real-time wind speed and direction data, storm forecasts, and other meteorological information.
Utilizing Emergency Management Resources:
- Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA): FEMA offers various resources to help individuals and communities prepare for hurricanes. Their website provides valuable information on evacuation plans, emergency supply kits, and disaster response mechanisms.
- Local emergency management agencies: Each state or region typically has its own emergency management agency that releases updated hurricane advisories and evacuation instructions. Staying connected with these agencies ensures timely access to crucial information that can aid in tracking hurricanes.
Hurricane Tracking Equipment And Technology:
- Weather radar systems: Advanced weather radar technologies like Doppler radar enable meteorologists to determine the direction, intensity, and size of a hurricane. These systems provide real-time data on precipitation, wind speed, and storm structure.
- Hurricane Hunter aircraft: The National Hurricane Center employs specialized aircraft, such as the famous “Hurricane Hunters,” to collect data from inside hurricanes. These flights gather information on atmospheric conditions, wind speeds, and storm features, helping to enhance forecast accuracy.
- Weather buoys and floats: These devices are deployed in the ocean to collect valuable data, including sea surface temperature, wave height, and atmospheric pressure. This information contributes to improving hurricane tracking models and forecasts.
Data Sources For Real-Time Storm Monitoring:
- Global Telecommunication System (GTS): The GTS facilitates the rapid exchange of meteorological information between countries. It ensures the availability of real-time data from sources worldwide, enabling accurate tracking of hurricanes.
- Satellites: Satellites provide critical data on hurricanes, including cloud cover patterns, sea surface temperatures, and atmospheric conditions. This information aids forecasters in monitoring storm intensity, trajectory, and potential landfall areas.
- Remote sensing technologies: Ground-based remote sensing instruments, such as weather stations and weather balloons, collect atmospheric data required for effective hurricane tracking. Combined with satellite observations, these sources contribute to a comprehensive understanding of storm behavior.
By employing these essential tools, individuals and organizations can stay well-informed and prepared when tracking hurricanes. Whether accessing weather tracking websites, utilizing emergency management resources, or leveraging specialized equipment and advanced technologies, these tools play a vital role in safeguarding lives and mitigating the impacts of these formidable weather events.
Staying Safe During A Hurricane
One can ensure their safety during a hurricane by effectively tracking its movement and progression. By monitoring the hurricane’s path, individuals can make informed decisions regarding evacuation, preparedness, and response measures. Stay updated with reliable sources and utilize tracking tools to stay ahead of the storm.
When a hurricane is approaching, it is crucial to prioritize the safety of yourself and your loved ones. To ensure your well-being, there are several essential steps you should take, including preparing an emergency supply kit, developing an evacuation plan, securing your home and property, and understanding storm surge and flood risks.
Let’s delve into each of these aspects in detail:
Preparing An Emergency Supply Kit:
- Stock up on non-perishable food items such as canned goods and dry snacks.
- Keep an ample supply of clean water, allowing for at least one gallon per person per day.
- Include a manual can opener and utensils in your kit.
- Pack a first aid kit with essential supplies like bandages, antiseptic solutions, and medications.
- Remember to include a flashlight, spare batteries, and a battery-powered radio to stay informed about the hurricane.
Developing An Evacuation Plan:
- Familiarize yourself with evacuation routes in your area.
- Identify safe locations where you can seek refuge during a hurricane.
- Arrange a meeting point for your family members in case you get separated.
- Prepare a list of emergency contacts including family, friends, and local authorities.
- Ensure that your vehicle is in good condition and has a full tank of gas in case evacuation becomes necessary.
Securing Your Home And Property:
- Trim trees and remove loose branches to minimize potential damage.
- Reinforce windows and doors with storm shutters or plywood.
- Clear your gutters and downspouts to allow for proper water drainage.
- Secure outdoor objects that may become hazardous during high winds.
- Consider investing in a generator to ensure a stable power supply during the storm.
Understanding Storm Surge And Flood Risks:
- Stay informed about the storm surge and flood risks associated with hurricanes.
- Follow any evacuation orders or advisories issued by local authorities.
- Be aware of your home’s vulnerability to flooding based on its location.
- Familiarize yourself with the flood warning system in your area.
- Avoid walking, driving, or swimming in floodwaters, as they could be contaminated or possess unseen hazards.
By taking these necessary precautions, you can increase your safety and reduce the potential risks associated with hurricanes. Remember to stay informed by monitoring weather forecasts and official updates from local authorities. Your preparedness and vigilance can significantly contribute to minimizing the impact a hurricane may have on you and your community.
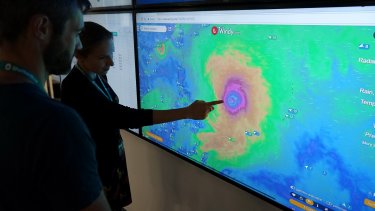
Credit: shelterbox.org
Frequently Asked Questions For How To Track Hurricanes
What Is The Best Source For Hurricane Tracking?
The best source for hurricane tracking is the National Hurricane Center’s website and their official tracking maps.
How Early Can A Hurricane Be Tracked?
Hurricanes can be tracked as early as a few days to a week before they make landfall.
Is There A Weather App That Tracks Hurricanes?
Yes, there are weather apps available that track hurricanes. They provide real-time updates.
How Are Hurricanes Tracked For Kids?
Scientists use satellites, planes, and buoys to track hurricanes. They collect data on the storms’ location, wind speed, and intensity.
Conclusion
Tracking hurricanes is an essential step in understanding and preparing for the impacts of these powerful storms. By utilizing a combination of advanced technology, reliable data sources, and various tracking tools, we can monitor hurricanes with greater accuracy and timeliness.
The data collected through these tracking methods can help meteorologists provide more accurate forecasts and early warnings, allowing communities to make informed decisions and take necessary precautions to protect lives and property. From satellite imagery and radar systems to mobile apps and websites, there are numerous resources available for individuals to stay updated on the progress of hurricanes.
By staying informed and following the guidance of trusted authorities, we can navigate through hurricane seasons with greater confidence and resilience. Remember, preparation is key, and tracking hurricanes is an essential part of being prepared for these powerful and unpredictable natural events.
Stay safe and be vigilant during hurricane season!
- What Is the 11 Hour Limit: A Comprehensive Guide - June 7, 2024
- What Happens if You Drive on a Suspended License in Virginia - June 7, 2024
- Wilcox Justice Court Overview: Online Services & Legal Proceedings - June 6, 2024